What is DNS?
Domain Name System
DNS is the phonebook of the internet, human access information online through names.
Web browsers access websites through website names, but how does it do it?
Each device connected to the internet has a unique IP address, which other machines use to find the device.
DNS eliminates the need for human memorize for for IP addresses, such as (ipv4 - -192.168.1.1)
How does DNS Works ?
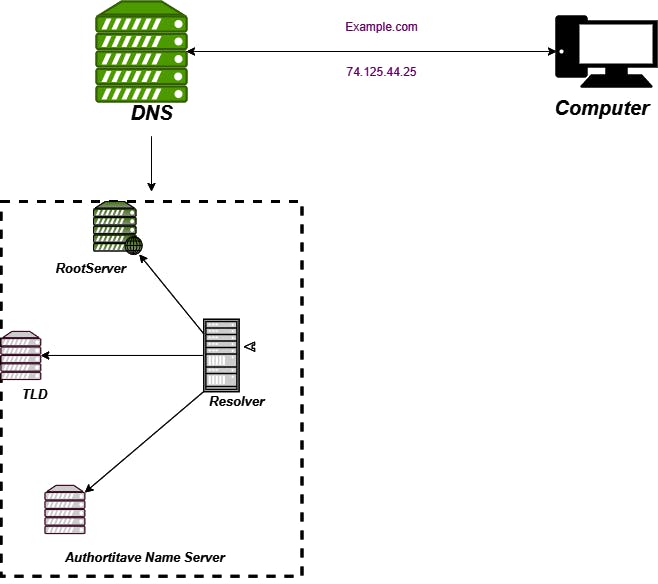
The process of DNS resolution involves converting a hostname (Such as - Example.com) into a friendly IP address (such as - 192.168.1.1)
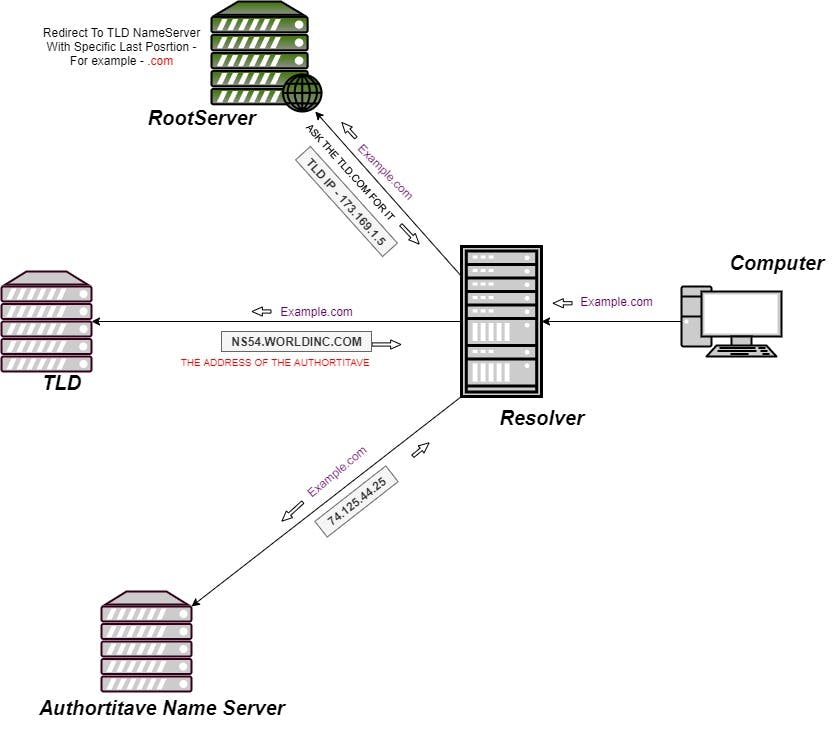
On webpage load, the computer asks the resolver for the IP address of the website name.
The resolver can't find the IP address of the website we are searching for, so it will send a message to the root server,
The root server knows everything, but it can't detect the IP address of the desirable website name.
The root server directs the message to the DNS TLD NameServer.
DNS TLD NameServer (TOP Level Domain) can be thought a specific rack of books in a library, this NameServer is the next step in the search for a specific IP address. it hosts the last portion of a hostname, (in Example.com, the TLD server is .com)
The last step in finding a specific website IP address is the Authoritative DNS server.
The authoritative name server is responsible for knowing everything about the domain, whatever
The authoritative name server including the IP address of the last portion.
Let me show you a diagram , this will help you to understand the flow
How does the Domain name server, find the IP Address?
Good to know - About the Servers.
ROOT SERVER
The top of the root, of the DNS hierarchy.
13 sets of these root servers strategically placed around the world
Operated by 12 different organizations
Each set has their own unique IP address
TLD NameServer
Stores the address information for the top-level domains
Such as .com - .net - .org. etc...
Authoritative NameServer
Responsible for knowing everything about the domain
Including the IP address
